Core vs. Headline Inflation
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Core vs. Headline Inflation
✔ GS Paper 3 (Indian Economy & Monetary Policy) ✔ Current Affairs – RBI’s Inflation Targeting Framework ✔ Impact on Economic Growth & Price Stability
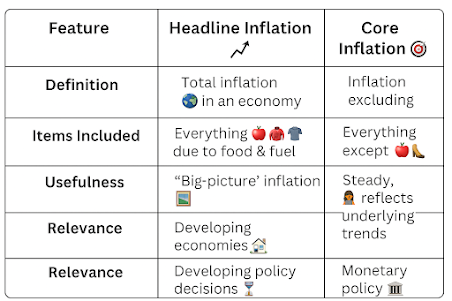
Headline Inflation 📈 – Broad Measure of Inflation
Definition: Measures total inflation across the economy, including all goods and services.
Includes: Food 🍎, Fuel ⛽, Manufactured Goods 🏭, Services 💼.
Volatility: Highly fluctuating due to seasonal variations in food & fuel prices.
Key Index Used: Consumer Price Index (CPI) & Wholesale Price Index (WPI) in India.
Core Inflation 🎯 – Stable Measure for Monetary Policy
Definition: Measures inflation trends by excluding volatile items like food & fuel.
Purpose: Provides a steady 🔥 and long-term inflation trend for policy decisions.
Derived From: Headline Inflation minus food & fuel components.
Importance: Used by RBI for monetary policy decisions (Inflation Targeting Framework – 4% ± 2%).
Key Differences
Feature | Headline Inflation 📈 | Core Inflation 🎯 |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
UPSC Significance – Why This Matters?
✅ GS Paper 3 – Indian Economy: Understanding inflation management crucial for RBI’s policy decisions.
✅ Monetary Policy: RBI uses Core Inflation as a basis for repo rate adjustments under inflation targeting.
✅ Impact on Welfare Schemes: High Headline Inflation affects food subsidies, PMGKAY, and MNREGA budgets.
is ✅ Current Affairs: Inflation trends influence interest rates, fiscal policy, and economic growth projections.
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps



Comments