"Learning Today, Leading Tomorrow" शिक्षिका एवं संकलक – Poornima Gontiya 📖 विषय शामिल हैं: अंतर्राष्ट्रीय संगठन मध्य प्रदेश सामान्य ज्ञान विटामिन एवं स्वास्थ्य भारतीय संविधान भारतीय दण्ड संहिता (IPC) 🌀 भाग 1 : अंतर्राष्ट्रीय संगठन (International Organizations) संयुक्त राष्ट्र संघ (UNO) की स्थापना कब हुई थी? (A) 1919 (B) 1945 (C) 1939 (D) 1950 UNICEF का मुख्य उद्देश्य क्या है? (A) शिक्षा (B) बच्चों का कल्याण (C) शांति स्थापना (D) चिकित्सा WHO का मुख्यालय कहाँ स्थित है? (A) पेरिस (B) जेनेवा (C) लंदन (D) न्यूयॉर्क IMF का पूरा नाम क्या है? (A) International Money Fund (B) International Monetary Fund (C) International Management Fund (D) International Member Fund UNESCO का मुख्यालय कहाँ है? (A) लंदन (B) पेरिस (C) बर्लिन (D) वॉशिंगटन विश्व बैंक की स्थापना कब हुई थी? (A) 1944 (B) 1950 (C) 1960 (D) 1972 SAARC की स्थापना किस वर्ष हुई थी? (A) 1985 (B) 1980 (C) 1990 (D) 1975 WTO का मुख्य उद्देश्य क्या है? (A) विश्व शांति (B) अंतर्राष्ट्रीय व्...
PESA ACT
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
IMAGE SOURCE - GOOGLE
The Provisions of the Panchayats (Extension to the Scheduled Areas) Act, 1996, abbreviated as the PESA Act, is a significant law enacted by the Government of India. Its purpose is to ensure self-governance through traditional Gram Sabhas for people residing in the Scheduled Areas of India123.
Here are some key points about the PESA Act:
Objective: The PESA Act aims to empower local communities in Scheduled Areas by recognizing their right to govern themselves through their own systems of self-government. It also acknowledges their traditional rights over natural resources4.
Extension of Part IX of the Constitution: The provisions of Part IX of the Constitution, which relate to Panchayats, are extended to the Scheduled Areas subject to certain exceptions and modifications1.
Features and Modifications:
- Customary Law and Practices: State legislation on Panchayats in Scheduled Areas must be in consonance with the customary law, social and religious practices, and traditional management practices of community resources.
- Village Definition: A village typically consists of a habitation, group of habitations, hamlet, or group of hamlets, managed according to traditions and customs.
- Gram Sabha: Every village must have a Gram Sabha comprising individuals whose names are on the electoral rolls for the village-level Panchayat.
- Gram Sabha Responsibilities:
- Approve plans, programs, and projects for social and economic development before implementation by the village-level Panchayat.
- Identify beneficiaries under poverty alleviation and other programs.
- Certify utilization of funds by the Panchayat.
- Reservation of Seats: Seats in the Scheduled Areas’ Panchayats are reserved in proportion to the population of communities seeking reservation. The reservation for Scheduled Tribes must not be less than half the total number of seats, and all Chairperson seats are reserved for Scheduled Tribes.
- Nomination of Representatives: The State Government may nominate persons from Scheduled Tribes without representation in intermediate or district-level Panchayats1.
In summary, the PESA Act empowers local communities in Scheduled Areas, ensuring their active participation in governance and resource management through traditional Gram Sabhas4
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Popular posts from this blog
The Jogimara and Sitabenga Caves
image source- PURATATTVA The Jogimara and Sitabenga Caves , also known as the Sitabenga Cave or Jogimara Cave , are ancient cave monuments nestled in the north side of the Ramgarh hills in Puta village, Chhattisgarh, India . These remarkable caves date back to approximately the 3rd-century BCE to 1st-century BCE and hold significant historical and artistic value 1 . Here are some fascinating details about these caves: Non-Religious Inscriptions and Ancient Frescoes : The Jogimara and Sitabenga Caves are notable for their non-religious inscriptions in Brahmi script and Magadhi language . They also feature one of the oldest colored frescoes in Asia . Scholars debate whether the Sitabenga cave was an ancient performance theater or a resting place along an ancient trade route. Some consider it the oldest performance theater on the Indian subcontinent ...
What is Underfueling?
Underfueling is a form of anxiety and the form of physical as well as mental stress that impacts health and training of a sportsman in a negative way. (From the source of motivrunning.com) Signs of Underfueling Moderate: Constant hunger Fatigue, low energy levels Irritability Intense cravings, or constant focus on food Trouble sleeping Hunger pangs during workouts Gastrointestinal (GI) distress Muscle cramps or weakness Severe: Hypothermia (cold intolerance) Stress fractures Changes in, or complete loss of, a regular menstrual cycle (for women) Significant weight loss The following fueling tips are general, catered to the average population. To understand your individual needs, consult with a sports dietitian. Eat before exercising, especially for high intensity workouts and long runs Eat during exercise if the workout exceeds 60-75 minutes (I generally recommend fueling every 35-40 minutes) Eat after exercising, a recovery meal or snack, followed by another meal or snack within a few ...
Core vs. Headline Inflation
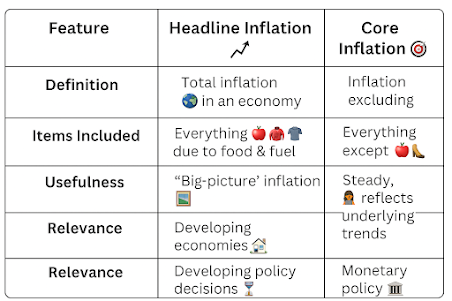
Core vs. Headline Inflation ✔ GS Paper 3 (Indian Economy & Monetary Policy) ✔ Current Affairs – RBI’s Inflation Targeting Framework ✔ Impact on Economic Growth & Price Stability Headline Inflation 📈 – Broad Measure of Inflation Definition : Measures total inflation across the economy, including all goods and services. Includes : Food 🍎, Fuel ⛽, Manufactured Goods 🏭, Services 💼 . Volatility : Highly fluctuating due to seasonal variations in food & fuel prices. Key Index Used : Consumer Price Index (CPI) & Wholesale Price Index (WPI) in India. Core Inflation 🎯 – Stable Measure for Monetary Policy Definition : Measures inflation trends by excluding volatile items like food & fuel . Purpose : Provides a steady 🔥 and long-term inflation trend for policy decisions. Derived From : Headline Inflation minus food & fuel components. Importance : Used by RBI for monetary policy decisions (Infla...
.jpg)


Comments